The Role of Hot-Dip Galvanizing in Long-Lasting Infrastructure
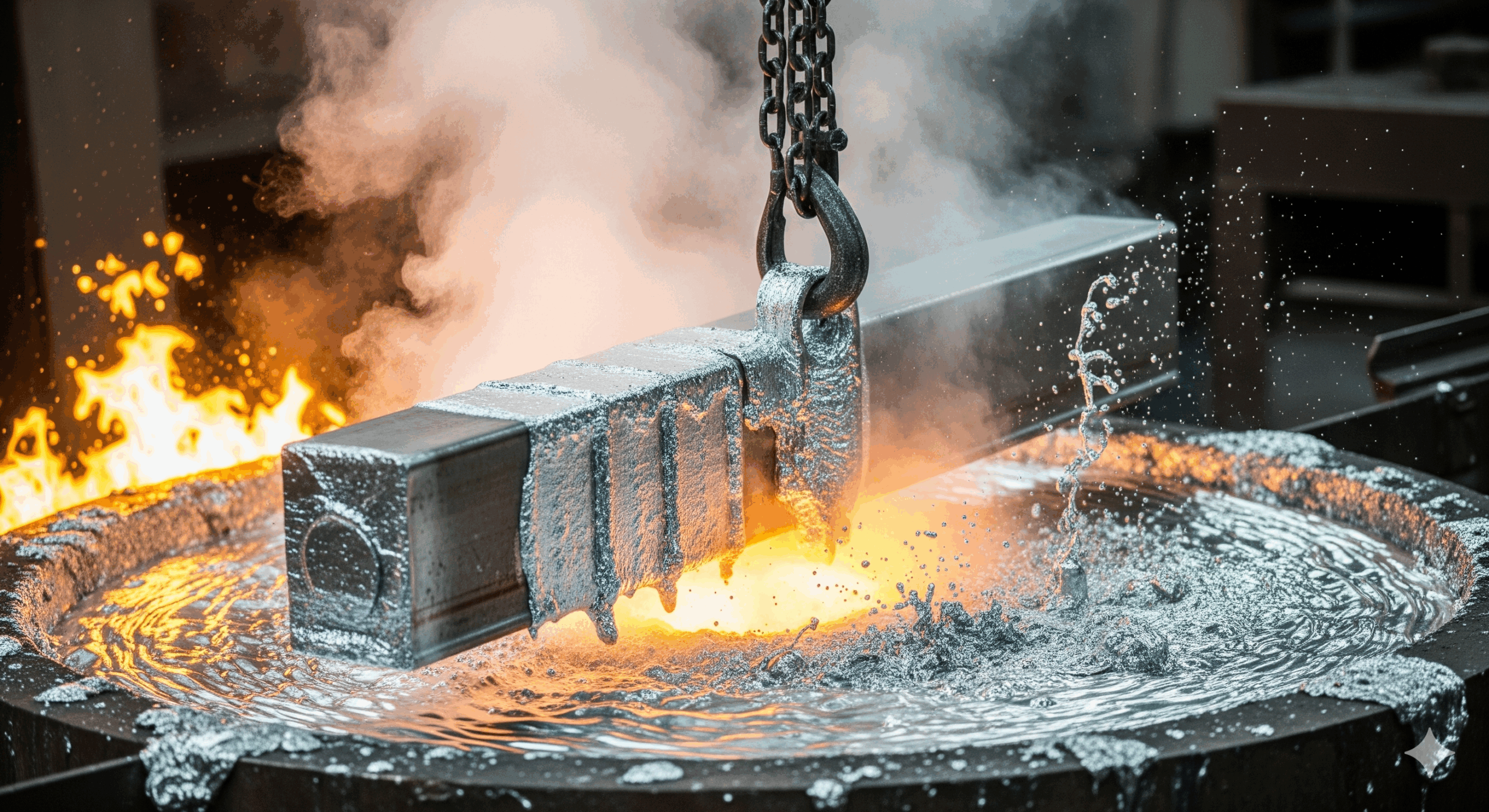

In the infrastructure and power sector, durability and reliability are critical. From transmission towers to substation structures, every component must withstand harsh environmental conditions for decades. One of the most effective ways to ensure this is through hot-dip galvanizing (HDG).
Hot-dip galvanizing is a process where steel structures are coated with a layer of zinc by immersing them in a molten zinc bath. This protective coating prevents corrosion, enhances structural life, and reduces long-term maintenance costs. For industries that depend on reliability, such as power transmission and renewable energy, galvanizing is not an option but a necessity.
Benefits of Hot-Dip Galvanizing
- Corrosion Resistance: Zinc forms a barrier against moisture and chemicals, preventing rust.
- Long Service Life: Galvanized steel structures can last 30–50 years depending on the environment.
- Cost-Effective: Minimizes maintenance and replacement costs over time.
- Sustainability: Zinc is recyclable, making HDG eco-friendly.
Applications in Power & Infrastructure
Hot-dip galvanizing is widely used for:
- Transmission line towers up to 765 kV
- Substation structures and gantries
- Solar module mounting structures
- Wind mill lattice towers
- Chemical plant and PEB structures
Hevins’ Expertise in Galvanizing
At Hevins Engineering Pvt. Ltd., we operate an automated 8-meter galvanizing bath with strict temperature controls, ensuring uniform quality. Our annual galvanizing capacity exceeds 24,000 MT, making us capable of handling large-scale projects with ease. We comply with domestic and international standards (IS, BSEN, ASTM) to deliver products that meet client expectations.
By choosing hot-dip galvanizing, companies not only enhance the life of their infrastructure but also ensure safety, efficiency, and long-term value.
👉 Looking for reliable galvanizing services? Connect with Hevins today.